The Ever Increasing Alert Noise Problem
Modern hybrid-IT environments are monitored by numerous multi-vendor and multi-domain monitoring tools that generate humongous amounts of alerts and events, most of which are not readily actionable. The Industry term for this is “Alert Noise”.
Noisy alerts increase the risk of real alerts going undetected causing service outages. These alerts also carry siloed information missing the application or service context. Furthermore, NOCs are also inundated with tickets caused by such false alerts when routed directly to Incident Management Systems.
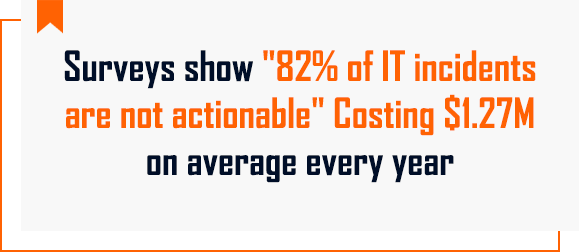
How does Alert Noise Impact the Organization?
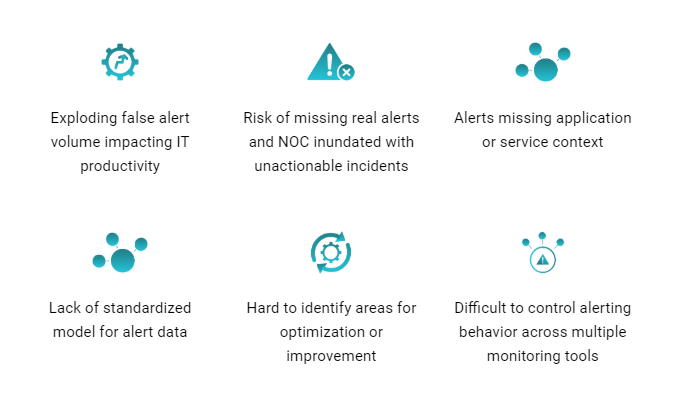
What is CloudFabrix Alert Watch?
The CloudFabrix Alert Watch serves as a digital gatekeeper for all your IT Alerts & Events, which can be ingested from all of your monitoring tools using featured integrations and APIs. Alert Watch then generates fewer actionable incidents by performing alert enrichment, deduplication, correlation and suppression. This helps in significantly reducing alert noise (up to 95%) and increases actionability of alerts.

How does CloudFabrix Alert Watch Work?
To understand the functioning of how an Alert is ingested to how alerts are clustered, refer CloudFabrix Alert Watch – A Digital Gatekeeper for All your IT Alerts & Events.
Each Alert is grouped into a specified Cluster using various Machine Learning techniques like HDB scan (Hierarchical Density Based Clustering), etc. Correlation and Suppression are two kinds of groups created based on Enriched attributes. Clustering does not create a correlated group alert until instructed. Clustering or ML algorithms are used to create a Correlation Policy to club several alerts or events together as a single incident. The analytics engine deployed creates a Correlation group out of the umpteen events generated. All the alerts in a specified correlation group are categorized as a single incident.
Correlation in CloudFAbrix Alert Watch
Correlation is the process of grouping or relating similar variables in a specified dataset. There are two types of Correlation policies used in the CloudFabrix Alert Watch module, the Correlation Alert Group Policy and the Correlation Alert Burst Policy.
The Correlation Alert Grouping is the Grouping of various Alerts based on their time of occurrence, severity level of occurrence and other specific criterion.
There are 3 factors determining the Correlation Alert Group Policy,
- The policy has a specific time interval for an alert to be categorized in a specific group. Once the time interval has expired, the alert is grouped into the next defined group.
- The filter selects the alerts as per the specified criterion, only if the group filter criterion is satisfied, the alert is added to that group.
- Group policy is assigned a severity level and is grouped as per the given specified metric like critical severity, major severity, minor severity or warning severity.
When there are several alerts generated continuously in a specified time interval, it’s called an Alert Burst. Additionally for Correlation Alert Burst policy, timing is a major criterion. The Raise rate or rate of arrival or rate of occurrence of the Alert is the most essential criterion.
The Correlation performed on such Alert Bursts is dependent on the following factors,
- The time interval is specified and number of alerts in the specified time on a repetitive basis is the most important factor
- The policy has a specific time interval for an alert to be categorized in a specific group. Once the time interval has expired, the alert is grouped into the next defined group.
- The filter selects the alerts as per the specified criterion, only if the group filter criterion is satisfied, the alert is added to that group.
- Group policy is assigned a severity level and is grouped as per the given specified metric like critical severity, major severity, minor severity or warning severity.
Suppression in CloudFabrix Alert Watch
In the case of correlation policies we create alert groups and each group creates an incident. Suppression policy suppresses the alerts as defined by the policy. The filters for Suppression policy are based on clusters, timing, etc.
The differentiating factor is scheduling for Suppression, Suppress when flapping – there are cases where VPN is used to connect to the network, it gets disconnected and connected continuously, causes repetitive issues, that condition is called Suppression when Flapping
To learn more about CloudFabrix Alert Watch, visit AI for Alerts.